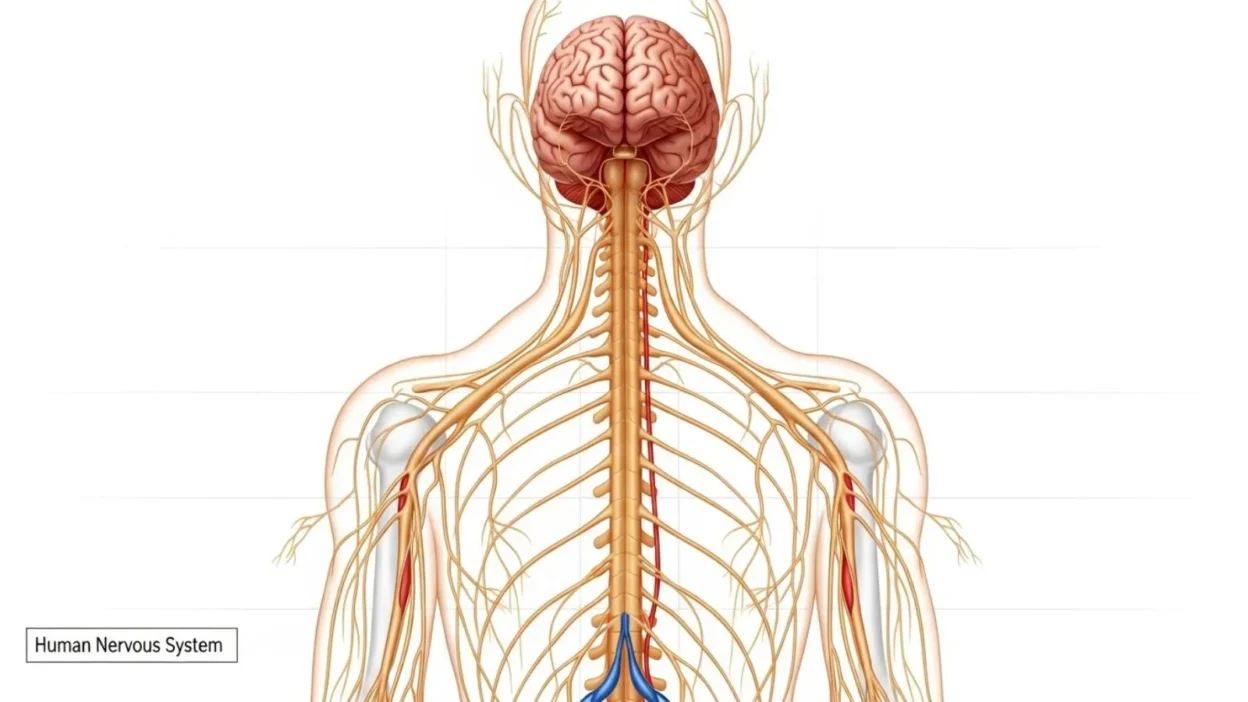
Have you ever wondered how your body reacts instantly when you touch something hot or how you can think, move, and feel all at the same time? The answer lies in your nervous system a complex network that acts like your body’s communication superhighway.
Every sensation you feel, every movement you make, and even the automatic functions like heartbeat and digestion are controlled by this incredible system. Many people search for “what does the nervous system do” because they want to understand how it works, why it’s essential, and what happens when it malfunctions.
From controlling voluntary actions like walking to regulating involuntary functions such as breathing, the nervous system plays a vital role in every aspect of life.
In this article, we will explore its structure, functions, common disorders, and ways to keep it healthy, giving you a clear understanding of how this amazing system keeps your body running smoothly.
Nervous System Quick Answer
The nervous system is the body’s communication network, responsible for sending, receiving, and processing information from every part of the body. In simple terms, it acts like the command center, controlling how your body responds to the environment and maintains internal functions. When you touch a hot stove, your sensory nerves immediately send a signal to your brain, which processes the information and instantly tells your muscles to pull your hand away. This all happens in a fraction of a second, showing how fast and efficient the nervous system is.
The system is divided into two main parts: the central nervous system (CNS), which includes the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), which consists of all the nerves connecting the CNS to the rest of the body. The CNS interprets information and makes decisions, while the PNS carries out these commands and relays sensory information back to the CNS.
The nervous system also controls both voluntary actions, like walking, writing, or speaking, and involuntary actions, like heartbeat, breathing, and digestion. Additionally, it enables reflexes automatic, rapid responses that protect the body from harm.
Understanding the nervous system helps explain how our body works and why it is essential for survival, coordination, and overall health. In the following sections, we will dive deeper into its structure, functions, disorders, and practical ways to maintain a healthy nervous system.
Structure of the Nervous System
The nervous system is a highly organized network, divided into two main parts: the Central Nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS). Understanding its structure is key to knowing how it controls every function in the body.
Central Nervous System (CNS)
The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord. The brain is the control center, responsible for thoughts, memory, emotions, decision-making, and coordinating movements. The spinal cord acts as a communication highway, transmitting messages between the brain and the rest of the body. Together, they process information and generate responses that allow you to interact with the world.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
The PNS includes all the nerves outside the CNS. Its primary function is to connect the CNS to your limbs, organs, and skin. The PNS is divided into two parts: somatic and autonomic. The somatic nervous system controls voluntary movements, like walking, typing, or picking up objects. The autonomic nervous system manages involuntary functions such as heart rate, digestion, and breathing.
Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System
The autonomic system has two divisions: sympathetic and parasympathetic. The sympathetic division triggers the “fight or flight” response during stressful situations, while the parasympathetic division promotes “rest and digest,” helping the body recover and maintain balance.
How the Nervous System Works
The nervous system works like an intricate communication network, allowing your body to respond quickly and efficiently to both internal and external stimuli. Its basic unit is the neuron, a specialized cell that transmits information using electrical and chemical signals. Neurons connect with one another through synapses, tiny gaps where neurotransmitters carry messages from one cell to the next. This process enables your brain and body to coordinate nearly every action.
There are three main types of neurons: sensory neurons, which carry information from sensory organs like the skin, eyes, and ears to the brain; motor neurons, which transmit instructions from the brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands; and interneurons, which connect neurons within the CNS to process information and coordinate responses.
When you touch something hot, sensory neurons immediately send a signal to your spinal cord. Sometimes, the signal triggers a reflex arc, where your spinal cord instantly tells your muscles to pull your hand away before the brain even processes the information. This rapid response protects the body from injury.
Beyond reflexes, the nervous system also controls complex actions, such as thinking, problem-solving, and voluntary movements. Every sensation, thought, and motion involves a coordinated network of neurons transmitting billions of signals every second. Understanding how neurons and signals work highlights the nervous system’s critical role in keeping the body functional, responsive, and adaptable to constantly changing environments.
Functions of the Nervous System
Sensory Function
The sensory function involves detecting changes both inside and outside the body. Specialized sensory receptors in the skin, eyes, ears, nose, and tongue gather information about temperature, pressure, pain, light, sound, and smell. These signals are sent to the brain and spinal cord, allowing the body to react appropriately. For example, feeling a hot surface triggers a message to the brain to move your hand away quickly.
Integrative Function
The integrative function occurs mainly in the brain and spinal cord. Here, the nervous system interprets incoming sensory information, makes decisions, and determines the best response. This function allows reasoning, memory formation, and emotional processing. For instance, when deciding whether to cross a busy street, your brain processes visual and auditory cues, integrating the information to ensure a safe decision.
Motor Function
The motor function involves sending instructions from the brain or spinal cord to muscles and glands, producing a response. This can be voluntary, like writing or walking, or involuntary, like adjusting heartbeat or releasing digestive enzymes. Reflex actions, such as blinking when something approaches the eye, also fall under motor function.
Importance of the Nervous System
The nervous system is vital for survival, coordination, and overall well-being. It acts as the body’s command center, ensuring that every organ, tissue, and muscle works together seamlessly. Without a properly functioning nervous system, the body would struggle to respond to even the simplest stimuli.
One of its primary roles is controlling body coordination and balance. Whether you’re walking on uneven ground, playing sports, or simply reaching for an object, the nervous system constantly processes sensory input and sends instructions to muscles to maintain stability and movement. It also regulates involuntary functions, such as breathing, heartbeat, and digestion, which are crucial for sustaining life without conscious effort.
The nervous system is essential for cognition, learning, and memory. It allows you to think, solve problems, and retain experiences that shape behavior and decision-making. Emotions and social interactions also rely heavily on proper nervous system function, influencing mood, empathy, and reactions to the environment.
Additionally, the nervous system provides reflexes, rapid responses that protect the body from harm. For example, touching a sharp object or stepping on a hot surface triggers an immediate reaction, preventing injury.
Damage to the nervous system can result in serious conditions, such as paralysis, memory loss, or impaired motor skills, highlighting its importance in everyday life. By understanding its critical role, we gain appreciation for how it keeps the body functional, responsive, and healthy, making it one of the most essential systems in the human body.
Common Nervous System Disorders
The nervous system, while highly efficient, can be affected by various disorders that disrupt its normal function. Understanding these conditions helps highlight the importance of keeping this system healthy.
One common disorder is Alzheimer’s disease, a progressive brain condition that affects memory, thinking, and behavior. It gradually impairs the ability to perform daily tasks and can lead to severe cognitive decline. Parkinson’s disease is another disorder that primarily affects movement, causing tremors, stiffness, and difficulty with balance and coordination due to the loss of dopamine-producing neurons.
Epilepsy is a neurological condition characterized by recurrent seizures caused by abnormal electrical activity in the brain. Seizures can vary from brief lapses in attention to violent convulsions, impacting daily life. Multiple Sclerosis (MS) affects the central nervous system by damaging the protective covering of nerves, leading to muscle weakness, numbness, and difficulty with coordination.
Other disorders include migraines, neuropathy, and stroke, each affecting different functions of the nervous system. Symptoms often include pain, weakness, numbness, loss of sensation, or cognitive impairment, depending on the affected area.
Preventing or managing nervous system disorders often involves a combination of medical treatment, lifestyle changes, and early diagnosis. Maintaining a balanced diet, regular exercise, proper sleep, and avoiding toxins like alcohol and drugs can reduce the risk of certain conditions.
By understanding common nervous system disorders, individuals can recognize symptoms early, seek proper treatment, and adopt healthy habits to protect this essential system that controls every aspect of life.
Interesting Facts About the Nervous System
The nervous system is full of fascinating features that make it one of the most complex and efficient systems in the human body. Understanding these facts can give a deeper appreciation of how it works.
One amazing fact is the sheer number of neurons in the human brain—approximately 86 billion—each forming thousands of connections called synapses. These neurons transmit signals at incredible speeds, up to 250 miles per hour, allowing the body to react almost instantly to stimuli. For example, reflex actions, like blinking when something approaches the eye or pulling your hand away from a hot surface, occur before the brain even consciously processes the event.
Another fascinating feature is neuroplasticity, the nervous system’s ability to adapt and reorganize itself. This means that the brain can form new neural connections in response to learning, experience, or injury. It’s why people can recover from certain brain injuries or continue learning new skills throughout life.
The nervous system also manages complex tasks simultaneously, such as coordinating movement while processing sensory input and maintaining balance. Even the involuntary actions, like heartbeat, breathing, and digestion, happen without conscious thought, demonstrating the system’s efficiency.
Finally, the brain and spinal cord are protected by layers of tissue and fluid, yet they remain incredibly delicate and sensitive, emphasizing the need for proper care. These fascinating characteristics show just how critical and remarkable the nervous system is, controlling every aspect of our daily lives, thoughts, movements, and reactions.
How to Keep Your Nervous System Healthy
Maintaining a healthy nervous system is essential for overall well-being, as it controls everything from movement and reflexes to emotions and memory. Simple lifestyle choices can have a significant impact on keeping this system functioning optimally.
1. Eat a Balanced Diet:
Nutrients like Omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins B, C, D, and E, and minerals such as magnesium and zinc support nerve health and brain function. Foods like fish, nuts, leafy greens, and whole grains are excellent choices.
2. Exercise Regularly:
Physical activity increases blood flow to the brain, improves coordination, and strengthens neural connections. Exercises such as walking, swimming, or yoga also reduce stress, which can negatively affect nervous system health.
3. Get Enough Sleep:
Sleep is crucial for the nervous system to repair itself and consolidate memories. Aim for 7–9 hours of quality sleep per night to allow neurons to recover and function properly.
4. Manage Stress:
Chronic stress can impair nervous system function, leading to anxiety, memory problems, or nerve damage. Techniques like meditation, deep breathing, and mindfulness help maintain balance in the autonomic nervous system.
5. Avoid Toxins:
Limiting alcohol, avoiding recreational drugs, and reducing exposure to environmental toxins protect nerve cells from damage.
6. Mental Stimulation:
Engaging in learning, puzzles, reading, or new skills keeps the brain active and encourages neuroplasticity.
Nervous System in Everyday Life
The nervous system is at work in almost every aspect of daily life, often without us even realizing it. It allows the body to sense, respond, and adapt to the environment quickly and efficiently.
For example, when driving, your nervous system coordinates multiple actions at once: your eyes monitor the road, your hands control the steering wheel, and your brain processes traffic signals and nearby vehicles to make split-second decisions. Similarly, when cooking, you rely on the nervous system to sense temperature, control hand movements, and maintain balance, all while planning your next steps.
Even simple tasks, such as typing on a keyboard or picking up a cup of coffee, require precise communication between the brain, spinal cord, and muscles. Reflexes, like blinking when something approaches your eyes or pulling your hand from a hot surface, protect you from harm before conscious thought occurs.
The nervous system also regulates involuntary actions that are crucial for survival, such as breathing, heartbeat, and digestion. Emotional experiences, like happiness, fear, or excitement, are processed and expressed through neural activity, showing how deeply connected the nervous system is to both body and mind.
From learning new skills and playing sports to responding to danger or enjoying music, the nervous system ensures that every sensation, thought, and movement occurs smoothly. Its seamless coordination is essential for daily life, highlighting its critical role in keeping the body and mind functional, responsive, and adaptive.
FAQs:
1. What is the main function of the nervous system?
The nervous system controls and coordinates all body activities. It allows the body to sense, interpret, and respond to internal and external stimuli, including movement, reflexes, emotions, and involuntary functions like heartbeat and digestion.
2. What are the main parts of the nervous system?
The nervous system has two main parts: the central nervous system (CNS), consisting of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), which connects the CNS to the rest of the body. The PNS includes the somatic system for voluntary actions and the autonomic system for involuntary functions.
3. How does the nervous system send messages?
Messages are sent through neurons, specialized cells that transmit electrical and chemical signals. Sensory neurons carry information to the brain, motor neurons send instructions to muscles or glands, and interneurons connect and process information within the CNS.
4. What are common nervous system disorders?
Disorders include Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, neuropathy, and stroke. Symptoms vary but may include memory loss, tremors, seizures, numbness, or difficulty moving.
5. How can I keep my nervous system healthy?
Maintaining a healthy nervous system involves a balanced diet, regular exercise, proper sleep, stress management, avoiding toxins, and mental stimulation. These habits support neuron function and overall brain health.
Conclusion:
The nervous system is the body’s master control center, responsible for every sensation, thought, movement, and reflex.
From coordinating voluntary actions like walking or typing to regulating involuntary functions such as heartbeat, breathing, and digestion, it ensures that the body works efficiently and responds to the environment.
Its two main divisions, the central and peripheral nervous systems, work together seamlessly, allowing communication between the brain, spinal cord, and the rest of the body.
Understanding the nervous system also highlights the importance of maintaining its health.
A balanced diet, regular exercise, sufficient sleep, stress management, and avoiding harmful substances all support optimal function and prevent disorders.

I’m the mind behind Jokesattack.com, your go-to place for daily laughs, clever puns, and hilarious memes. Spreading smiles one joke at a time!