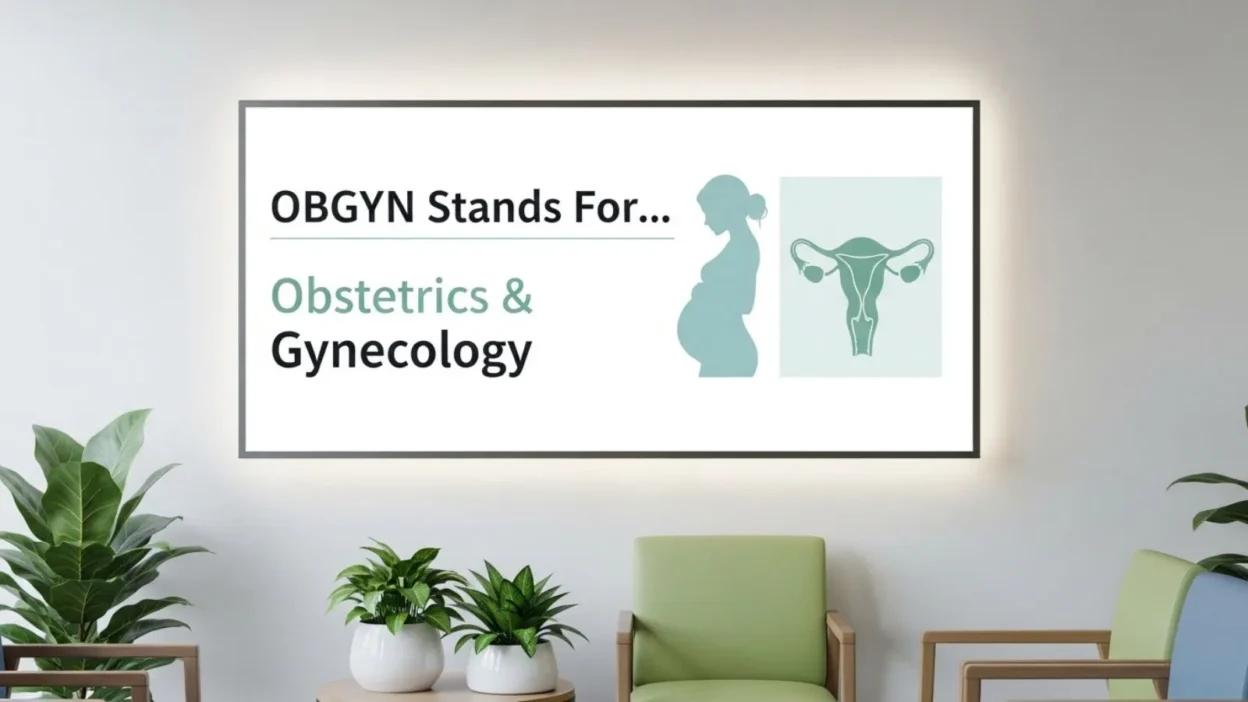
When you see the term OBGYN on a hospital sign, medical report, or appointment slip, it’s normal to wonder what it actually means.
Medical abbreviations can feel confusing, especially if you’re visiting a doctor for the first time, planning a pregnancy, or dealing with women’s health concerns. That’s why many people search “what does OBGYN stand for” to get a simple and clear explanation.
An OBGYN plays an important role in women’s healthcare at different stages of life from the teenage years to pregnancy, childbirth, and menopause.
Understanding the OBGYN meaning helps you feel more confident about your health decisions and medical care.
In this article, we’ll explain the OBGYN full form, break down what obstetrics and gynecology mean, and explore what an OBGYN does. By the end, you’ll know exactly when you might need an OBGYN and why this medical specialty is so important for long-term reproductive health.
What Does OBGYN Stand For? (Full Form Explained)
The term OBGYN stands for Obstetrics and Gynecology, which are two closely related medical specialties focused on women’s health. Because these areas overlap so often, doctors are usually trained in both, and that combined specialist is known as an OBGYN.
Obstetrics is the branch of medicine that deals with pregnancy, childbirth, and care after delivery. An obstetrician supports women throughout pregnancy, monitors the health of both mother and baby, manages labor and delivery, and provides postpartum care. This includes routine prenatal checkups, ultrasounds, and addressing pregnancy-related complications.
Gynecology, on the other hand, focuses on the overall health of the female reproductive system. A gynecologist treats conditions related to the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, and hormones. This includes menstrual problems, pelvic pain, fertility issues, contraception, and menopause care. Gynecology also involves preventive screenings such as Pap smears and pelvic exams.
When these two specialties are combined, the doctor is called an OBGYN. This means they are trained to care for women both during pregnancy and throughout their non-pregnant years. Understanding the OBGYN full form helps clarify why this type of doctor is so commonly recommended for women’s healthcare. Whether it’s routine checkups, pregnancy care, or reproductive health concerns, an OBGYN provides comprehensive and continuous medical support.
What Is an Obstetrician?
An obstetrician is a medical doctor who specializes in caring for women during pregnancy, childbirth, and the period immediately after delivery. Their main focus is to ensure the health and safety of both the mother and the baby throughout the entire pregnancy journey. Obstetricians are trained to handle normal pregnancies as well as high-risk situations.
During pregnancy, an obstetrician provides regular prenatal checkups to monitor the baby’s growth and the mother’s health. This includes tracking weight, blood pressure, and fetal development, as well as ordering ultrasounds and lab tests. They also help manage common pregnancy symptoms such as nausea, swelling, and fatigue, while watching for potential complications like gestational diabetes or high blood pressure.
When it’s time for labor and delivery, an obstetrician is responsible for managing the birth process. They assist with vaginal deliveries and are trained to perform cesarean sections (C-sections) if needed. In emergency situations, obstetricians can quickly make medical decisions to protect both mother and child.
After childbirth, obstetricians continue care during the postpartum period. This includes checking physical recovery, monitoring bleeding, addressing pain, and providing guidance on breastfeeding and emotional health. While obstetricians focus mainly on pregnancy-related care, many are also trained as gynecologists, which is why most women see an OBGYN for complete reproductive healthcare.
What Is a Gynecologist?
A gynecologist is a medical doctor who specializes in the health of the female reproductive system. Unlike obstetricians, gynecologists focus on women’s health outside of pregnancy. Their care supports patients from adolescence through adulthood and into menopause, making them an important long-term healthcare provider.
Gynecologists diagnose and treat conditions related to the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, cervix, and vagina. Common concerns include irregular periods, painful menstruation, hormonal imbalances, pelvic pain, and reproductive infections. They also help manage chronic conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), endometriosis, and uterine fibroids.
Preventive care is a major part of a gynecologist’s role. Routine exams such as pelvic exams and Pap smears help detect issues early, including cervical cancer and other reproductive health problems. Gynecologists also provide guidance on birth control options, sexual health, and family planning based on individual needs and lifestyle.
In addition, gynecologists support women through major life stages like puberty, fertility planning, and menopause. During menopause, they help manage symptoms such as hot flashes, mood changes, and hormonal shifts. They may also offer screenings for bone health and overall wellness.
Many gynecologists are trained in obstetrics as well, allowing them to become OBGYNs. This combined training ensures patients receive comprehensive care, whether they need routine reproductive health support or pregnancy-related medical attention.
What Does an OBGYN Do? (Roles and Responsibilities)
An OBGYN is a medical doctor trained in both obstetrics and gynecology, which allows them to provide complete reproductive and pregnancy-related care. Their responsibilities cover a wide range of services, making them a key healthcare provider for women at every stage of life.
One of the main roles of an OBGYN is preventive care. This includes routine checkups, pelvic exams, Pap smears, and breast exams to detect health issues early. These visits help monitor reproductive health and reduce the risk of serious conditions such as cervical cancer or hormonal disorders.
OBGYNs also diagnose and treat various medical conditions. They manage menstrual irregularities, pelvic pain, infections, fertility issues, and hormonal imbalances. For patients planning a family, OBGYNs provide guidance on conception, prenatal vitamins, and healthy pregnancy preparation.
During pregnancy, an OBGYN closely monitors both the mother and the baby. This includes prenatal visits, ultrasounds, lab tests, and managing pregnancy-related complications. When it’s time for delivery, they assist with labor and childbirth and perform C-sections if medically necessary.
After childbirth, OBGYNs provide postpartum care, focusing on physical recovery, emotional well-being, and family planning. They also help women navigate menopause by offering treatment options for symptoms like hot flashes and hormonal changes. Overall, an OBGYN plays a vital role in long-term women’s healthcare and wellness.
When Should You See an OBGYN?
Knowing when to see an OBGYN is essential for maintaining women’s health at every stage of life. OBGYNs are not just for pregnancy—they provide care for a wide range of reproductive and general health concerns.
For most women, the first OBGYN visit is recommended during adolescence, usually between ages 13 and 15, or when menstrual cycles begin. This helps establish a baseline for reproductive health, addresses puberty-related questions, and provides guidance on preventive care like vaccinations and screenings.
Women planning to become pregnant should see an OBGYN for preconception counseling. This includes assessing overall health, reviewing medications, and learning about prenatal vitamins and lifestyle adjustments to increase the chances of a healthy pregnancy. Once pregnant, regular prenatal visits with an OBGYN ensure proper monitoring of the baby’s growth, maternal health, and early detection of complications.
Routine checkups are also important for adult women, even if they are not pregnant. OBGYNs manage menstrual irregularities, pelvic pain, hormonal changes, and contraceptive needs. They also screen for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and perform preventive tests such as Pap smears and breast exams.
Later in life, OBGYN care continues through perimenopause and menopause, helping women manage symptoms like hot flashes, hormonal imbalance, and bone health concerns.
In short, you should see an OBGYN for preventive care, reproductive planning, pregnancy, or any concerns related to your reproductive health. Regular visits empower women to take control of their health and address issues early, improving long-term well-being.
Difference Between Obstetrician, Gynecologist, and OBGYN
Understanding the difference between an obstetrician, a gynecologist, and an OBGYN helps you choose the right healthcare provider for your needs. While these terms are related, each has a specific focus.
An obstetrician specializes in pregnancy, childbirth, and postpartum care. Their main role is to ensure the health and safety of both mother and baby throughout pregnancy. Obstetricians provide prenatal care, manage labor and delivery, and handle pregnancy-related complications. They focus primarily on maternal and fetal health during this period.
A gynecologist, on the other hand, focuses on non-pregnancy aspects of women’s reproductive health. Gynecologists treat menstrual issues, hormonal imbalances, pelvic pain, fertility concerns, and reproductive system disorders. They also perform routine screenings such as Pap smears, breast exams, and pelvic exams to prevent or detect diseases early.
An OBGYN combines both fields. This means they are trained as both an obstetrician and a gynecologist, allowing them to provide comprehensive care. OBGYNs can manage pregnancies from conception to postpartum, while also addressing general reproductive health issues. This dual training makes OBGYNs the most versatile choice for women seeking complete care.
Knowing these differences is important when scheduling appointments. If you are pregnant or planning a pregnancy, you may specifically need an obstetrician or an OBGYN. For routine reproductive health checkups, a gynecologist or OBGYN is suitable. Ultimately, an OBGYN offers a one-stop solution for lifelong women’s healthcare, combining the expertise of both specialties.
Common Conditions Treated by an OBGYN
An OBGYN is trained to manage a wide variety of conditions related to women’s reproductive health and pregnancy. Understanding these common conditions can help you know when to seek medical care and what to expect during visits.
During pregnancy, OBGYNs monitor for complications such as gestational diabetes, high blood pressure, preeclampsia, and preterm labor. They ensure both the mother and baby remain healthy and intervene if any issues arise.
Beyond pregnancy, OBGYNs address menstrual disorders like irregular periods, heavy bleeding, or painful menstruation. Hormonal imbalances, including polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), are also commonly treated. These conditions can affect fertility, weight, and overall well-being, so proper management is essential.
OBGYNs also handle reproductive system infections, including bacterial or yeast infections and sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like chlamydia or HPV. Early detection and treatment prevent complications and maintain reproductive health.
Other common issues include endometriosis, fibroids, and ovarian cysts, which can cause pelvic pain, heavy bleeding, or fertility problems. OBGYNs offer both medical and surgical treatment options depending on severity.
In addition, OBGYNs provide preventive care such as Pap smears, pelvic exams, and breast screenings, which help detect cancer or other serious conditions early.
Common Tests and Procedures Performed by an OBGYN
OBGYNs perform a variety of tests and procedures to monitor, diagnose, and maintain women’s reproductive health. These procedures help detect issues early, guide treatment, and support overall well-being.
One of the most common procedures is the pelvic exam, where the doctor examines the reproductive organs to check for abnormalities. This often includes a Pap smear, which screens for cervical cancer by detecting abnormal cells early. Regular Pap smears are essential for early detection and prevention.
Ultrasounds are another routine test. Obstetricians use them during pregnancy to monitor fetal development, detect complications, and confirm gestational age. Gynecologists may also use ultrasound to evaluate ovarian cysts, fibroids, or other reproductive issues.
Prenatal testing is crucial for pregnant patients. Tests like blood work, glucose screenings, and genetic tests assess maternal and fetal health and help identify potential risks.
OBGYNs also perform minor surgical procedures, such as colposcopy (examining the cervix for abnormal cells), LEEP (removing precancerous cervical tissue), and endometrial biopsies. For reproductive or pregnancy-related concerns, OBGYNs may perform more advanced surgeries, including C-sections, hysterectomies, or laparoscopic procedures.
In addition to medical interventions, OBGYNs provide guidance on contraception and family planning procedures such as IUD insertion or sterilization.
OBGYN vs Midwife: What’s the Difference?
Many women wonder whether they should see an OBGYN or a midwife, especially when planning for pregnancy and childbirth. While both provide care related to pregnancy, their training, responsibilities, and scope of practice are different.
An OBGYN is a medical doctor trained in both obstetrics and gynecology. They handle high-risk pregnancies, perform surgical procedures like cesarean sections, and manage medical complications for both mother and baby. OBGYNs provide comprehensive reproductive care, including routine gynecological exams, preventive screenings, and management of chronic reproductive health conditions. Because of their medical training, they can quickly respond to emergencies during pregnancy or labor.
A midwife, on the other hand, is a trained healthcare professional who specializes in supporting women during pregnancy, labor, and postpartum. Midwives often focus on natural childbirth and provide personalized care, including education on labor, breastfeeding, and postpartum recovery. They typically manage low-risk pregnancies and refer patients to an OBGYN if complications arise or if surgical intervention is needed.
The choice between an OBGYN and a midwife often depends on personal preference, medical history, and risk factors. Women seeking comprehensive medical oversight, especially with a high-risk pregnancy, may choose an OBGYN. Those desiring natural birth support and one-on-one attention may prefer a midwife.
Some healthcare systems encourage a collaborative approach, where a midwife and OBGYN work together to provide care, ensuring safety while supporting a positive birth experience. Understanding the differences allows women to make informed decisions about pregnancy and reproductive health.
How to Choose the Right OBGYN
Choosing the right OBGYN is an important decision for women’s health. A trusted OBGYN provides medical expertise, personalized care, and peace of mind for reproductive and pregnancy-related concerns. Here are key factors to consider when making your choice.
Experience and Specialization:
Look for an OBGYN with experience in areas relevant to your needs. Some specialize in high-risk pregnancies, fertility, or minimally invasive surgeries. Experienced doctors can handle complications efficiently and provide reliable guidance.
Hospital Affiliation:
Consider the hospital or clinic where the OBGYN practices. A well-equipped facility with high-quality maternity services ensures access to advanced care if needed.
Communication and Comfort:
Feeling comfortable with your OBGYN is essential. Choose a doctor who listens carefully, answers questions clearly, and respects your preferences. Trust and communication improve the overall healthcare experience.
Gender Preference:
Some women feel more comfortable with a male or female doctor. Consider your personal comfort, especially for intimate exams and discussions.
Availability and Accessibility:
Check the OBGYN’s schedule, office location, and response time. Ease of access is important for emergencies, regular appointments, and prenatal visits.
Referrals and Reviews:
Ask friends, family, or primary care doctors for recommendations. Online reviews can also provide insight into patient experiences and satisfaction.
Is an OBGYN a Doctor? (Education and Training)
Yes, an OBGYN is a fully licensed medical doctor who has completed extensive education and training in both obstetrics and gynecology. Becoming an OBGYN requires dedication, years of study, and rigorous hands-on experience to ensure they can provide safe, comprehensive care for women.
The journey begins with a medical degree, usually taking four years after completing an undergraduate program. During medical school, students study general medicine, anatomy, physiology, pharmacology, and clinical skills. After graduation, they enter a residency program in obstetrics and gynecology, which typically lasts four years. During residency, doctors gain practical experience in hospitals and clinics, caring for pregnant patients, performing deliveries, conducting surgeries, and managing gynecological conditions.
After residency, OBGYNs must pass licensing exams to practice medicine. In many countries, they can also become board-certified, which demonstrates expertise and adherence to high professional standards. Some OBGYNs pursue further subspecialty training, such as maternal-fetal medicine, reproductive endocrinology, gynecologic oncology, or minimally invasive surgery.
The combination of medical school, residency, licensing, and optional subspecialty training equips OBGYNs to handle complex pregnancies, surgical procedures, and reproductive health issues safely. Their dual training in obstetrics and gynecology makes them versatile, providing care throughout a woman’s life—from adolescence and fertility planning to pregnancy, childbirth, and menopause.
FAQs:
1. What does OBGYN stand for in medical terms?
OBGYN stands for Obstetrics and Gynecology. Obstetrics deals with pregnancy, childbirth, and postpartum care, while gynecology focuses on women’s reproductive health.
2. Do men need an OBGYN?
OBGYNs specialize in female reproductive health, so men do not typically need an OBGYN. Men have their own specialists, like urologists, for reproductive and urinary health.
3. Is an OBGYN only for pregnancy?
No. While OBGYNs manage pregnancy care, they also handle routine gynecological exams, menstrual issues, hormonal concerns, fertility guidance, menopause management, and preventive screenings.
4. How often should you see an OBGYN?
For healthy adult women, a routine checkup once a year is recommended.
5. Can an OBGYN be your primary doctor?
While OBGYNs provide comprehensive reproductive and women’s health care, they usually do not replace a primary care doctor for overall health. Some patients, however, rely on their OBGYN for routine women’s health needs.
6. What is the difference between an OBGYN and a gynecologist?
A gynecologist focuses only on reproductive health, while an OBGYN is trained in both gynecology and obstetrics, allowing them to provide care during pregnancy as well.
Conclusion
Understanding what OBGYN stands for and the role these doctors play is essential for women’s health. An OBGYN, trained in both obstetrics and gynecology, provides comprehensive care throughout all stages of life from adolescence and routine reproductive health checkups to pregnancy, childbirth, and menopause.
They manage medical conditions, perform preventive screenings, guide family planning, and handle high risk situations when necessary.
Knowing the difference between an obstetrician, a gynecologist, and an OBGYN helps patients make informed choices about their healthcare.
Regular visits to an OBGYN empower women to monitor their reproductive health, detect issues early, and receive professional support for both physical and emotional well being.
If it’s pregnancy care, preventive screenings, or managing reproductive concerns, an OBGYN serves as a trusted partner in lifelong women’s health. By understanding their expertise, you can take control of your health with confidence and peace of mind.

I’m the author behind Jokesattack.com, where I share the funniest jokes, puns, and memes to make your day brighter with laughter. 😄🎉